A Brief History of Google Algorithm Updates that Killed Businesses
 In today’s modern era of information technology, search engine optimization has become the norm for a company’s online success. With Google holding a market share of 70% on PC and 87.59% on both smartphones and tablets, it’s no doubt that businesses should reconsider their SEO strategy in order to create Google-friendly websites.
In today’s modern era of information technology, search engine optimization has become the norm for a company’s online success. With Google holding a market share of 70% on PC and 87.59% on both smartphones and tablets, it’s no doubt that businesses should reconsider their SEO strategy in order to create Google-friendly websites.
Google has been consistently tweaking its ranking algorithm to ensure that only the most relevant websites are shown in the search results.
In 2011, Google rolled out the Panda update, followed by the Penguin update in 2012, Hummingbird in 2013, Pigeon in 2014, and Mobilegeddon in 2015. The results were absolutely dramatic for many businesses: while some have suffered a decrease in search engine ranking (and subsequently, a major drop in traffic), others have been completely erased from Google’s index.
What are the most notable Google algorithm updates that have killed many businesses throughout the years? Keep reading to find out.
1. Google Panda
Google has rolled out the Panda update back in February 2011. Intended to lower the rank of websites providing low-quality content that was of no use to users, the Panda algorithm update has reportedly affected the rankings of 12 percent of all search results. An increasing number of websites were trying to rank in search engines by publishing irrelevant, keyword-focused content that wasn’t delivering the information users were looking for. Some websites were publishing content just for the sake of driving more traffic, without paying attention to the accuracy of the information.
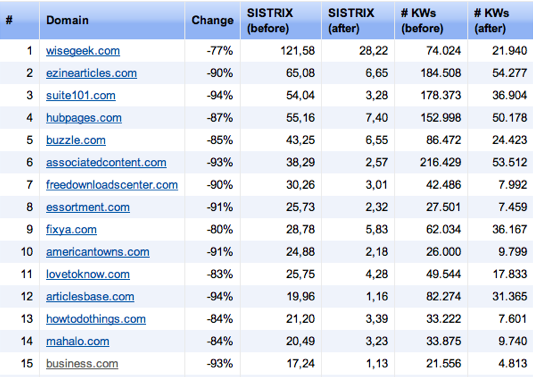
A great number of websites — many of which had been established for several years already — were impacted by the rollout of Google’s Panda update. Of them, content farms, also known as content mills (websites that publish low-quality, usually generalized content), were the most affected: Suite101, Demand Media, and Examiner to name a few. Article submission directories like Ezine Articles have also seen a major decrease in website traffic as of February 2011.
The table below shows a list of top 15 websites that have suffered the most after the Panda update has been rolled out:
 2. Google Penguin
2. Google Penguin
One of the most significant algorithm updates, Google Penguin has been rolled out in 2012 as a response to websites trying to manipulate their search engine ranking through link schemes (paid links, link networks etc).
According to Google’s estimates, the update has affected approximately 3.1% of queries. Since backlinks are one of the most important indicators of authority and can dramatically impact how a website ranks in Google, many webmasters have been employing unethical link building techniques.
Before Penguin was rolled out in April 2012, these techniques proved very efficient, helping low-quality websites outrank high-quality ones.
In response to webmasters’ attempts to game the algorithm to rank higher in search engines, Google has rolled out Penguin. One of the most notable example of big brand that has been affected by the Penguin update is Rap Genius — they invited bloggers to add links to its lyrics content in exchange for Rap Genius tweeting about their posts. The result? Rap Genius has been penalized on Christmas Day in December 2013.
Another relevant example is Interflora — after conducting a Valentine’s Day campaign with advertorials posted across a variety of websites. All advertorials were pointing back to Interflora’s website. This could have been a perfectly fine strategy if the links had been applied the “nofollow” attribute, but since the company’s goal was to attract more visitors, all links were dofollow.
3. Page Layout Algorithm Update
Also known as Top Heavy Update, the page layout algorithm update was rolled out by Google in January 2012. The update was aimed to penalize websites with too many ads or too little content above the fold. Users looking for information want to be able to access the information without scrolling down the page past a slew of ads. While placing ads above the fold is not prohibited, websites that load the top of their pages with ads and provide a bad user experience stand a chance at getting penalized by Google.
4. Mobilegeddon
Rolled out in April 2015, the Mobilegeddon was one of the biggest algorithm updates we’ve seen so far. Intended to offer users a better experience by decreasing the ranking of non-mobile-friendly websites in search engines, Mobilegeddon has impacted many well-known websites such as Huffington Post UK.
With more and more users accessing the web from their smartphones and tablets, it makes sense that websites should tailor their websites so they’re mobile-friendly and can be successfully accessed from just any device. If a website is not mobile optimized, users will have a hard time reading the text and navigating, which will dramatically impact their experience. Statistics show that most users will abandon websites that are not mobile ready.
The table below shows a list of websites that ranked higher, and respectively lower after the Mobilegeddon algorithm update was rolled out in April 2015.
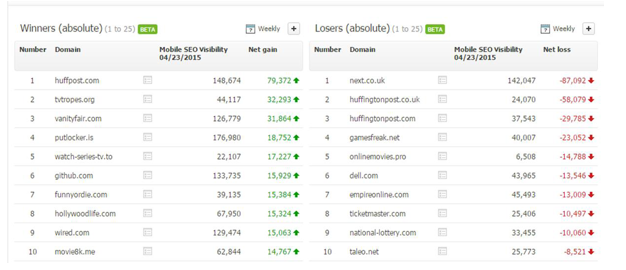
How does Google define a website that’s mobile friendly? A website that doesn’t use software that’s not common on mobile devices, has text that’s readable without zooming, sizes content to the screen so no horizontal scrolling or zooming is needed, and places links far enough apart so they can be correctly tapped — these are the factors that Google uses to determine if a website is mobile ready.
With Google continually rolling out algorithm updates, it’s no doubt that the SEO scene is changing at a fast pace. Businesses need to effectively adhere to Webmaster Guidelines in order to rank high in search engines, otherwise they stand a chance at getting penalized. Even some of the biggest brands and businesses out there have been touched by these algorithm updates. For example my aerospace marketing website Martinwilson.me often ranks above established sites in the spaceflight industry, such as Aviationweek.com and SpaceNews.com, who only recently rebuilt their websites to be mobile friendly. – if Google doesn’t spare them, how can we expect it to spare websites with a comparatively smaller audience and lower traffic?
If your website has been affected by one of these algorithm updates, it’s important that you or your SEO consultant identify the cause of the penalty and address it as soon as possible. Then you can send a reconsideration request through Google Webmasters Tools, so your website can get its ranking back.

